Introduction
Banking is a very sensitive yet challenging business. It is
not only about doing business but also about emerging itself as a safeguard of
public money and valuables. In the process to perform its duties and safeguard public money, the bank has to function effectively and in a well-controlled manner.
Such an effective and controlled manner to perform duties is possible through the identification
of risks and their effective management. Risk is usually referred to as
the potential financial or non-financial loss that the bank can suffer due
to the happening of certain adverse events. Banks can face major risks like the risk
of financial loss, risk of bad customer onboarding, risk of regulatory
non-compliance, risk of liquidity shortage, risk of bad credit disbursement,
risk of external fraud, risk of capital insufficiency, etc.
Lines of Defense
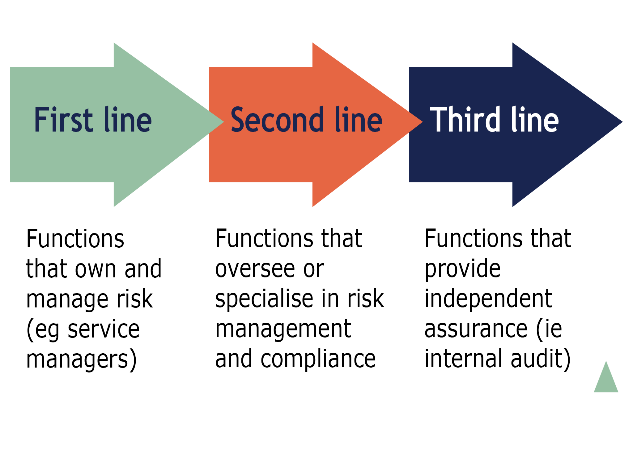
Bank has three lines of defense, the first line are the business
verticals, the second line is the Risk and Compliance verticals and the third line is
the Internal Audit. These three verticals should function parallelly for the bank’s
growth. The primary responsibility to manage risk is that of the business verticals
itself as they are the first line to defend against risks, after the first line comes, the Risk
and Compliance department which is the second line to defend the risk. And
finally, there is an internal audit which acts as a last line to check,
correct, suggest, and manage the risk as the third line of defense.
Types of Risk
To understand risk management, we need to first
understand the major risks that the bank can face. Here is the list of major
risks to which the bank is exposed:
1.
Credit Risk
2.
Operation Risk
3.
Market and Liquidity Risk
4.
IT /Digital Risk
Risk Management
Risk Management is the process of managing the risk
prevailing across the bank functions and implementing adequate controls to keep
such risk at an acceptable level. Risk Management is often referred to as a proactive measure adopted by a bank to safeguard its business. The Risk
management philosophy has been emphasized in detail by NRB Directive No. 5.
a. Management of Credit Risk
Credit Risk is the risk that the credit portfolio of the bank
deteriorates. Credit risk is the risk that the loan extended by the bank is not
recovered at all. When a borrower does not comply with the agreed credit terms
at the time of disbursement including default in payment, collateral dispute
and other defaults, credit risk starts to arise. Credit Risk gives raise to an increase in NPL, default in repayment, increase in recovery actions, etc. among
others. Exposure to Credit Risk will increase the bank’s Risk Weighted Exposure
and can put stress to bank’ capital. Managing the credit risk starts from
lending decision itself, Relationship Managers at branches shall have to access
the borrowers in detail to judge whether it will trigger to credit risk or not.
Branches shall have to access cash flows of the borrower, repayment
Possible Measures to Manage Credit Risk
i.
Evaluate 5C’s prior to lending (Capacity,
Character, Capital, Collateral, Conditions).U
ii.
Understand the need of borrower and ensure that
the financial need is genuine.
iii.
Evaluate the primary source of income, alternate
source of income and obtain assurance on repayment capacity.
iv.
Monitor the cash flows of the borrower and
safeguard bank against the cash flows regulatory.
v.
Get versed with regulatory compliance and offer
the credit product in line with approved bank’s product paper guidelines.
vi.
Monitoring and setting appetite of
Non-Performing Loan, overdue loans, expired loans to keep the portfolio mix
clean and recovery actions at low level.
vii.
Monitor the loan portfolio post disbursement,
carry out AMR (Account Monitoring Report) to evaluate the performance of the
accounts.
viii.
Understand the BASEL norms on assigning the
lending wise Risk Weighted Exposure and classify the credit portfolio as per
BASEL norms.
ix.
Verify
the customer details with regulator portal like IRD, ICAN for independent
assessment.
x.
Carry out
Credit Risk Review and judge the credit portfolio status.
xi.
Evaluate
the collateral, carry out CSVR, independently assess the market rate and ensure
its acceptability to bank and salability in future.
xii.
Carry out business visit and understand the
business process, receivable cycle, collection period, stock turnover time and
other sources of cash flows.
xiii.
Evaluate the CICL report, Declaration from
borrower, internally maintained Hotlist to check the borrower eligibility/history/capacity,
collateral backup, financial capacity, character of the borrower to minimize
the credit risk upfront. Borrower’s business / income shall be assessed through
account statement maintained with us or with another BFI’s. Every staffs
involved in credit chain shall have to be well versed with regulatory provisions,
NRB directives, internal policy and circulars to effectively manage the credit
risk. NRB directive no.1, 2 and 3 contains major regulatory provision with
regard to credit flow, credit risks and other credit parameters. Bank has an
independent Risk Management Department and Credit Approval Unit for effective
management of credit risk. For sound management of credit risk bank has
formulated several policies like Credit Policy, Risk Management Policy among
others. To buffer the effect of credit risk, bank implements BASEL framework
for assigning credit risk weight on credit exposure and link it with Capital to
compute CAR. Sometimes ineffective management of credit risk can lead to bank’s
failure like that of Lehman Brothers.
b.
Management of Operation Risk
Operation Risk, is the risk that arise because of inadequate
people, failed process, failed system and insufficient controls. Operation Risk
is more related to operation and functionality of banking operations. If a bank
fails to manage its day to day operation due to failed process, system,
controls or inadequate people then it results to operation risk. The primary
responsibility to manage operations at branch is that of Service Manager. So,
branch operation risk is the more inclined towards service managers, teller
operations, CSD staffs. Unlike credit risk, operation risk does not have a risk
weight assigned based on its exposure, rather the Basic Indicator Approach is
being used to assign risk weight in operational risk. Bank’s gross income of
past three years is taken to base for computation of operational risk weight
exposure as per BASEL norms. Thus, operation risk cannot be linked one to one
basis as like under credit portfolio. Operation Risk created by people can be
because of inadequate staff, staffs with fraud mindset etc. Operation Risk
created by process can be because of inadequate/obsolete policy documents, lack
of reporting line clarity, no approval process. Operation Risk created by
system can be because of outdated systems, weak system controls etc. whereas
operation risk created by external events can be because of external fraud,
natural calamities, riots etc. For effective operational risk management bank
shall train its staffs properly, define clear hierarchy line, set updated
policy and procedures, update and implement strong IT systems, carry out DR
drills, BIA test among others.
Possible Measures to Manage Operations Risk
i.
Understand the gravity of work, process defined
by bank, while performing tasks and be proactive rather than reactive.
ii.
Read all the regulatory policy, circulars,
directives, internal policies properly and understand/implement them in day to
day function.
iii.
Take ownership of every tasks so self- performed
iv.
Read major policies like Cash and Vault
Operation Manual, Customer Service Policy etc. related to operations.
v.
Ensure strict compliance to TAT and service
delivery.
vi.
Timely incident reporting and escalation for
resolution and effective settlement.
vii.
Monitor the suspicious activity of customers,
staffs and other stakeholders.
viii.
Maintain proper documentation and records to
ensure that the record keeping is safeguarded.
ix.
Ensure onboarding of customers is properly
monitored, documents are kept intact and risk grading is done to classify the
customer.
x.
Understand AML/CFT related risks properly and
evaluate the same while reviewing the funds flow of customers.
xi.
Take the maker and checker concept seriously in
systems and ensure dual custody of keys.
xii.
Supervise the work of subordinates, Consult with
supervisor for any confusion.
c.
Management of Market and Liquidity Risk
Market and Liquidity Risk, is the risk arising from the
macro-economic factors like interest rate change, currency movement and
liquidity position among others. Management of market and liquidity risk is
more determined by external factors and movement in market conditions. Market
and liquidity risk are managed through monitoring of Capital Adequacy, Net Open
Position, Investment analysis among others. Currently bank is adopting net open
approach to define risk weighted exposure for market and liquidity risk. Banks
analyzes its market position, investment position and foreign exchange exposure
among others to effectively manage the market and liquidity risk.
Possible Measures to Manage Market and Liquidity Risk
i.
Review the investment decision of the bank and
diversity the investment portfolio according to risk appetite of the bank.
ii.
Review the foreign exchange exposure and maintain
acceptable foreign exchange exposure in line with regulatory and internal
limit.
iii.
Evaluate fluctuations in domestic and
international currency, golds, NEPSE index etc. and its possible effect on
bank’s investment decision.
iv.
Review the bank’s capital position and its
adequacy commensurate to the growth decision taken by the bank.
v.
Monitor the industry and internal liquidity
position set internal limit commensurate to the bank’s size and growth
decision.
vi.
Evaluate concentration risks and diversification
in investment decision.
vii.
Interest rate movement monitoring and evaluation
to identify the possible effect on bank’s pricing decision.
viii.
Carry out GAP analysis and bucketing of possible
bank’s assets and liabilities.
ix.
Carry out the stress testing and analyze its
effects on bank’s major ratios and indicators.
x.
Review the regulatory limits and compare with
internal limit and identify possible risk areas.
xi.
Perform Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment
Test and evaluate the sufficiency of capital.
d.
Information Technology /Digital Risk
Information
Technology (IT) /Digital Risk, is the risk arising from various Information
Technology related factors. IT risks can arise because of hardware failure,
software failure, spams, virus attacks etc. IT security is a crucial part to
bank’s business and threat to IT protocol or security can have a serious affect
to bank’s business including its day to day operations. Modern banking is
heavily dependent on information technology systems including Servers,
Networks, CBS, Security among others. These IT ecosystems are exposed to risks
and management of possible risks to these systems is IT risk management. Modern
digital banking channels like mobile banking, web banking, ATM facility which
provide remote banking access to customers are exposed to financial loss risks,
data loss risks among others. For management of IT risks, bank has a separate
Information Security Officer under Risk Management Department to effectively
look after and minimize the risks.
Possible Measures to Manage IT (Digital) Risk
i.
Keep the IT credentials safe and not to share
the self IT credentials with other persons including supervisors.
ii.
Keep the PC system, IT platforms, HR system safe
with strong password.
iii.
Lock the PC or laptop while not in use to keep
it from mishandling.
iv.
Update the antivirus and other applications of
the system/ server periodically.
v.
Review the performance of third-party
application and software periodically.
vi.
Do not click or respond to messages/ mails from
unwanted/ unverified sources.
vii.
Maintain proper and timely backups of the core
application and must needed information servers.
viii.
Carry out IT audit for independent system
assessment and control review.
ix.
Review and independently check the digital IT
systems like mobile banking, web banking, IPS etc. and its gateway for its
effectiveness.
x.
Raise
awareness among customers for minimizing IT risks.
Is Risk Management Necessary?
Now, the question arise, is risk management really necessary
in banks. The answer is obvious; risk is inherent to bank’s business. After
discussing above risk areas, it can be concluded that as the bank’s business
grows the need of risk management is equally important.
Just take an example, if a customer arrives to your bank to
deposit Rs.1,000 and another customer arrives to your bank to deposit
Rs.9,00,000; the service delivery will definitely change. For a bank, deposit
of Rs.9,00,000 will make branch more liquid; yet the deposit of Rs.9,00,000
takes more precautions, more compliance requirement, requires double cash
counting, requires double the hassle as compared to that of Rs.1,000.
As in this example, as the business grows, more the
activeness and precautions shall be taken, so more than business more is the
requirement of prudent risk management.
Summary
As there is saying that no risk-no gain, Bank has to realize
that risk is inherent to business. To grow further, bank must have adequate
strategy ahead to manage the risk and shall have effective controls in place to
keep the risk at tolerable and acceptable limit.
Bank also sets risk appetite and risk tolerance limit based
on the its growth and nature cycle. Thus, as the bank’s business grows there is
an equal need of effective risk management. Bank shall equally emphasis on
growing the business and keeping its risk at tolerable limit as part for is
sustainable and long-term growth.



